Inquiry
Form loading...
The incorporation of Insolating Glass Acrylic Silicone in modern building designs plays a pivotal role in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), buildings account for approximately 40% of global energy consumption, highlighting the urgent need for innovative materials that can reduce this footprint. Insolating Glass Acrylic Silicone offers remarkable thermal insulation properties, reflecting up to 90% of solar radiation and significantly lowering cooling costs in warmer climates. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that improved insulation and window technologies can reduce energy use for heating and cooling by as much as 30-50%. As the construction industry increasingly shifts towards eco-friendly practices, leveraging materials like Insolating Glass Acrylic Silicone not only contributes to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions but also aligns with evolving regulatory standards aimed at promoting sustainable building solutions.
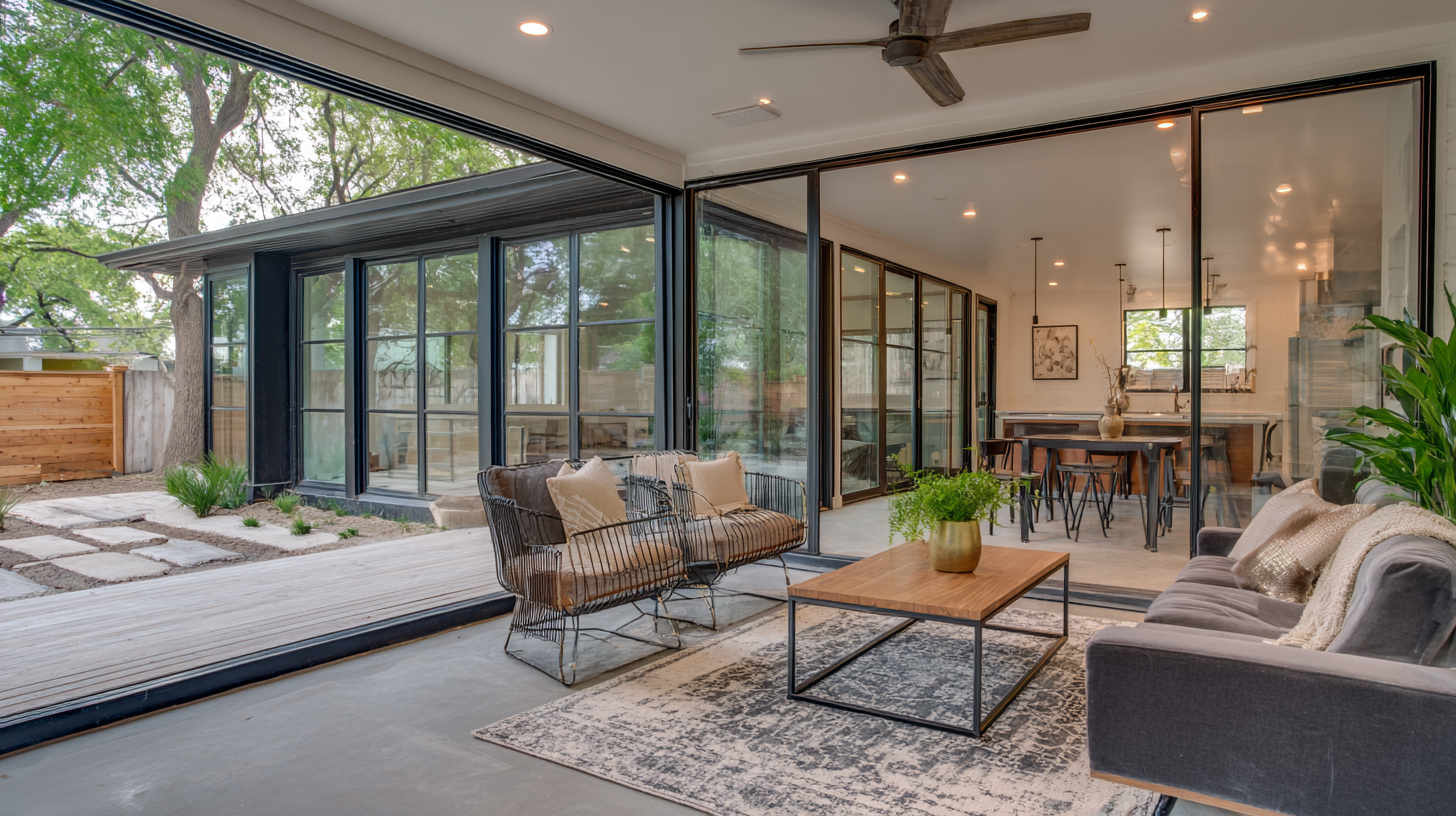
 Insolating glass acrylic silicone has emerged as a significant material in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability in modern architecture. Understanding its properties is crucial for designers and engineers looking to innovate in building façades. This composite material provides superior insulation and durability while maintaining transparency, which is vital for aesthetics and natural light dispersion in buildings. The recent advancements in high-strength bonding techniques for glass panes to aluminum frames with UV-resistant silicone adhesives demonstrate the growing trend of utilizing advanced materials to maximize energy efficiency.
Insolating glass acrylic silicone has emerged as a significant material in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability in modern architecture. Understanding its properties is crucial for designers and engineers looking to innovate in building façades. This composite material provides superior insulation and durability while maintaining transparency, which is vital for aesthetics and natural light dispersion in buildings. The recent advancements in high-strength bonding techniques for glass panes to aluminum frames with UV-resistant silicone adhesives demonstrate the growing trend of utilizing advanced materials to maximize energy efficiency.
Tips: When choosing insulators for your designs, consider the long-term benefits of using products with high mechanical strength and UV resistance. This ensures not only performance but also longevity in the façade. Furthermore, utilizing warm-edge spacers can significantly enhance the thermal performance of insulated glass systems, directly impacting energy consumption in buildings.
The shift towards eco-friendly materials, as exemplified by innovations like crystal clear silicone spacers, represents the industry's commitment to sustainability. As the demand for energy-efficient buildings increases, incorporating these advanced materials will play a crucial role in achieving better insulation and reducing the carbon footprint of new constructions.
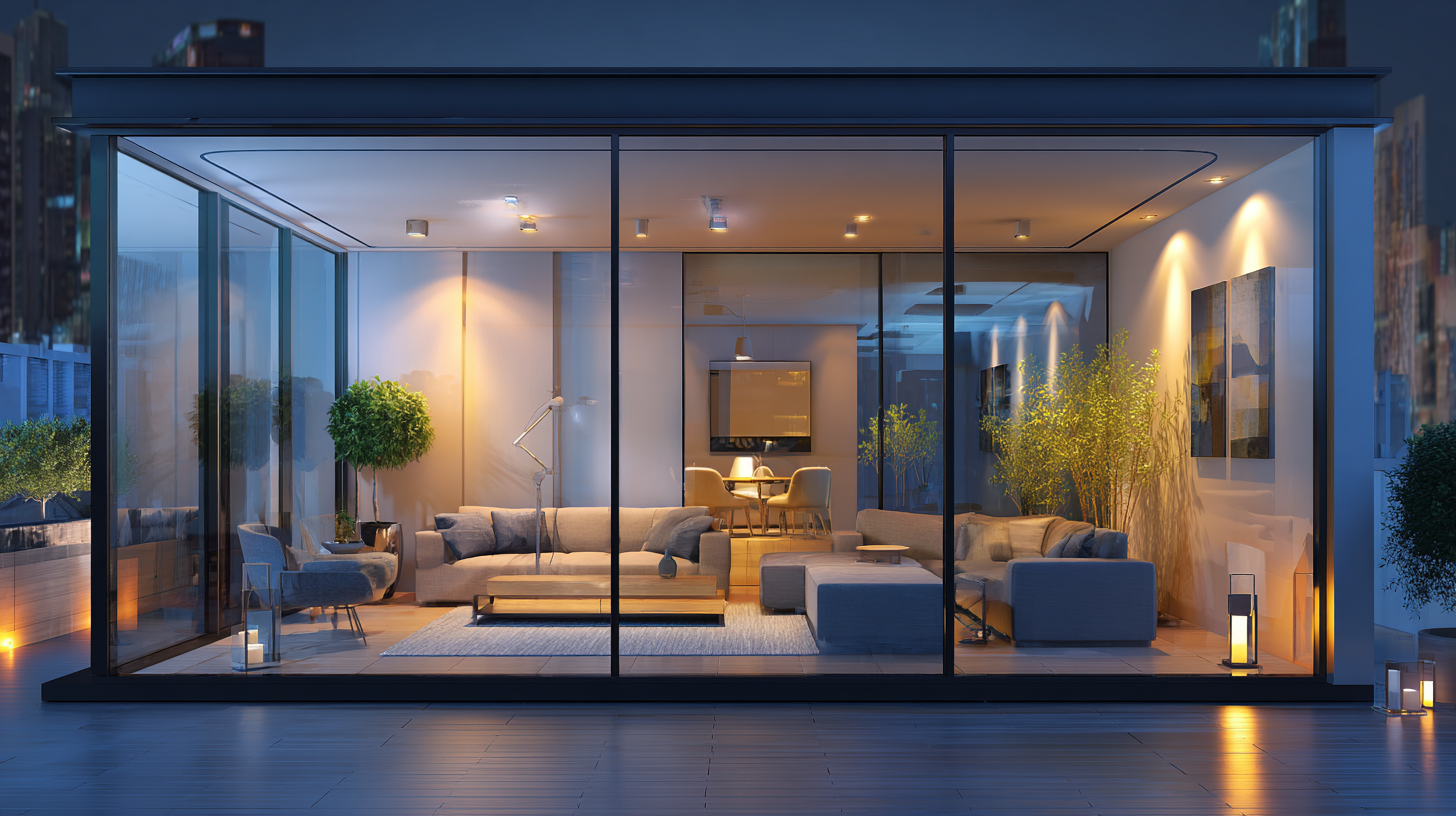 The integration of
insulative glass acrylic silicone
in building design has emerged as a vital strategy for enhancing energy efficiency. This innovative material functions by minimizing heat transfer, effectively reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling during extreme weather conditions. By providing superior thermal insulation, insulative glass acrylic silicone allows buildings to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while significantly lowering energy consumption. Consequently, architects and builders are increasingly incorporating this versatile material into their projects,
recognizing its potential to contribute to sustainable building practices.
The integration of
insulative glass acrylic silicone
in building design has emerged as a vital strategy for enhancing energy efficiency. This innovative material functions by minimizing heat transfer, effectively reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling during extreme weather conditions. By providing superior thermal insulation, insulative glass acrylic silicone allows buildings to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while significantly lowering energy consumption. Consequently, architects and builders are increasingly incorporating this versatile material into their projects,
recognizing its potential to contribute to sustainable building practices.
Beyond merely improving thermal performance, insulative glass acrylic silicone also offers
aesthetic versatility and durability,
making it an attractive choice for modern architecture. These properties not only enhance the visual appeal of structures but also ensure long-term sustainability by extending the lifespan of the building materials used. Additionally, the use of insulative glass acrylic silicone can lead to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels for heating and cooling. As a fundamental component of
energy-efficient building design,
insulative glass acrylic silicone plays a critical role in promoting sustainability in the construction industry.
The environmental impact of insulating materials is a crucial consideration in the quest for energy efficiency and sustainability in the building industry. According to a report from the U.S. Department of Energy, nearly 40% of energy consumption in the U.S. is attributed to residential and commercial buildings, highlighting the necessity for effective insulating solutions. Insulating glass acrylic silicone has emerged as a leading alternative, offering enhanced thermal performance that significantly reduces heating and cooling energy demands.
Using insulating materials intelligently not only improves energy efficiency but also contributes to lowering carbon footprints. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that improving insulation in buildings could facilitate emission reductions by up to 20% globally by 2030. Further, the lifecycle assessment of insulating glass acrylic silicone indicates that it has a lower environmental impact in terms of both production and end-of-life disposal compared to traditional insulating materials, promoting a more sustainable approach to construction and renovation activities. With advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainable building practices, incorporating these innovative insulating materials aligns with the urgent demands for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving environmental integrity.
In today's quest for energy efficiency and sustainability, insulative materials are becoming increasingly crucial. Insolating glass acrylic silicone is a revolutionary choice that significantly enhances thermal insulation, ensuring better energy retention within structures. This innovative material can help reduce heating and cooling costs, leading to substantial energy savings over time. Implementing these materials not only contributes to individual sustainability efforts but also aligns with broader environmental goals.
To maximize energy savings with insulative glass acrylic silicone, consider ensuring proper installation. A well-sealed installation can prevent air leaks, which are a common source of energy loss. Moreover, using double or triple glazing can further enhance the insulation properties. Regular maintenance is essential as well; clean the surfaces to maintain their transparency and thermal efficiency. Additionally, integrating these materials into energy-efficient designs, such as passive solar heating, can optimize their benefits, allowing for natural temperature regulation within spaces.
| Aspect | Benefits | Typical Energy Savings (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer | 20-30% | Lower carbon footprint due to reduced energy demand |
| Noise Reduction | Minimizes external noise interference | N/A | Improved living conditions enhance well-being |
| UV Protection | Protects interiors from fading | N/A | Extends the lifespan of furniture and interior items |
| Condensation Control | Reduces moisture buildup | N/A | Prevents mold growth and maintains indoor air quality |
| Cost Effectiveness | Reduces energy bills over time | 15-25% | Positive economic and environmental return on investment |
The future of energy efficiency technologies and materials is poised for significant transformation, particularly with the advent of innovative solutions such as perovskite solar cells. These cells, built from hybrid organic-inorganic halide materials, represent a breakthrough in solar technology thanks to their unique crystal structures that enhance the conversion of sunlight into electricity. As solar energy demand rises globally, the efficiency and affordability of perovskite solar cells may play a crucial role in making renewable energy more accessible and standardizing its use across diverse applications.
In parallel, the increasing emphasis on sustainability is driving advancements in various energy-efficient technologies. The integration of cutting-edge materials, including insulating glass and acrylic silicone, directly contributes to improved energy performance in buildings and products. These developments not only reduce energy consumption but also align with global decarbonization goals. Furthermore, the rapid evolution of electric vehicle technology emphasizes the need for advanced battery systems, reflecting a broader trend toward sustainable solutions in the automotive sector. Together, these innovations mark a promising future where energy efficiency and sustainability go hand in hand, paving the way for a resilient and eco-friendly energy landscape.
This chart illustrates the energy efficiency improvements associated with the implementation of insulative materials such as glass, acrylic, and silicone over a five-year period. The data reflects the average energy savings observed in residential buildings after applying these materials.