Inquiry
Form loading...
In recent years, the architectural industry has increasingly recognized the importance of energy efficiency and sustainability, leading to a surge in the adoption of innovative materials, notably Insolating Glass, Acrylic, and Silicone. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, buildings account for nearly 40% of total energy consumption in the United States, emphasizing the need for effective insulation solutions. Research indicates that using high-performance insolating materials can reduce energy costs by up to 30%, while also enhancing indoor comfort.

Moreover, the incorporation of Insolating Glass, Acrylic, and Silicone not only promotes superior thermal insulation but also provides aesthetic versatility. These materials allow architects to design with expansive glass facades, maximizing natural light while minimizing heat loss and gain. As the quest for sustainable building practices intensifies, understanding how to leverage these materials effectively will be crucial for modern architecture, ensuring both environmental responsibility and enhanced architectural beauty.
Insulating glass is a crucial component in modern architecture, as it significantly enhances energy efficiency and indoor comfort. According to the Narel, insulated glazing can improve thermal performance by up to 50%, reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems. This not only lowers energy costs but also diminishes the building's carbon footprint. The use of Low-E (low-emissivity) coatings further elevates this efficiency, reflecting heat back into the space during colder months and deflecting it outside during warmer months.

Moreover, the comfort level in modern buildings is greatly improved with insulating glass. A study by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory found that buildings with high-performance insulated windows recorded a 15% reduction in unwanted solar heat gains, leading to more stable indoor temperatures. This consistent environment not only enhances occupant comfort but also protects furnishings and finishes from damage due to fluctuating temperatures. By investing in high-quality insulating glass, architects and builders can create sustainable and comfortable living spaces that meet contemporary environmental and aesthetic standards.
Acrylic has emerged as a pivotal material in sustainable architectural design, offering numerous advantages over traditional glass. Its lightweight nature significantly reduces the structural load on buildings, leading to lower material use in construction and enhanced energy efficiency. By substituting heavier materials with acrylic, architects can also optimize transportation and installation processes, making construction projects faster and more environmentally friendly.
Moreover, acrylic provides excellent thermal performance, allowing for better insulation and reduced reliance on heating and cooling systems. This not only contributes to lower energy consumption during a building's lifecycle but also supports initiatives aimed at reducing carbon footprints. The transparency of acrylic allows ample natural light to penetrate, creating brighter indoor spaces while minimizing the need for artificial lighting. Thus, as architects aim to create designs that are both functional and sustainable, acrylic is proving to be an invaluable asset in the pursuit of modern architectural innovation.
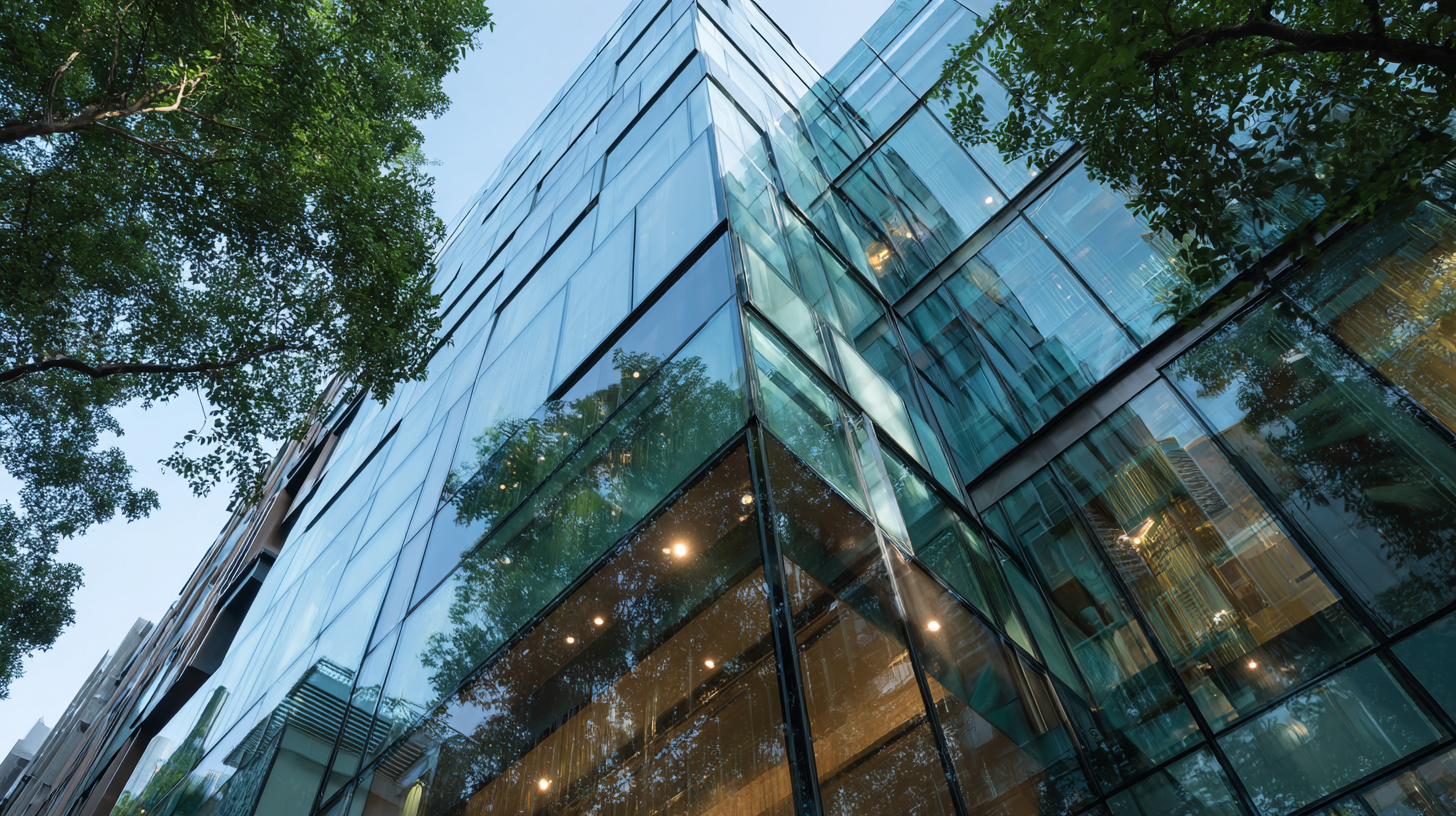 In modern architecture, silicone sealants have emerged as a vital component for enhancing energy efficiency. According to a recent market analysis, the adhesives and sealants market is projected to reach $70 billion by 2026, driven largely by construction applications. Silicone sealants, in particular, offer superior adhesion to diverse building materials, which is essential for structural glazing. As more architects aim for high-performance buildings, these sealants not only improve thermal insulation but also enhance UV stability, thereby extending the lifespan and efficiency of glazing systems.
In modern architecture, silicone sealants have emerged as a vital component for enhancing energy efficiency. According to a recent market analysis, the adhesives and sealants market is projected to reach $70 billion by 2026, driven largely by construction applications. Silicone sealants, in particular, offer superior adhesion to diverse building materials, which is essential for structural glazing. As more architects aim for high-performance buildings, these sealants not only improve thermal insulation but also enhance UV stability, thereby extending the lifespan and efficiency of glazing systems.
The demand for energy-efficient materials is evident in projects like the Deloitte Tower, which seeks LEED Platinum certification. This building utilizes energy-efficient glazing techniques that rely heavily on high-quality silicone sealants to meet stringent environmental standards. Industry reports indicate that investments in silicone technologies are increasing, as manufacturers recognize the need for advanced solutions that comply with modern sustainability goals. As a result, silicone sealants will continue to play a critical role in the construction sector, contributing to both architectural innovation and environmental stewardship.
Insulating materials play a crucial role in modern architecture, where energy efficiency and durability are paramount.
A comparative analysis of
glass, acrylic, and silicone demonstrates that each material has distinct advantages when it comes to cost savings and longevity.
According to a report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, building envelopes comprised of insulated glass can see energy savings between 20% to 40% compared to traditional single-pane alternatives.
This markedly reduces heating and cooling costs, making insulated glass a top choice for architects focusing on sustainability.
Acrylic, on the other hand, offers significant durability advantages.
Research from the American Society for Testing and Materials reveals that acrylic panels have a lifespan exceeding 30 years, outperforming many glass options in terms of shatter resistance and maintenance.
Silicone materials, while less commonly used for insulating, report impressive performance in sealing and thermal resistance.
A study published in the Journal of Building Physics indicates that silicone sealants can maintain their integrity after multiple freeze-thaw cycles, contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the structure.
As architects evaluate materials for modern projects, these metrics highlight the importance of selecting the right insulating solution for both cost-effectiveness and long-term performance.
As modern architecture continues to evolve, innovations in insulating materials play a pivotal role in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. The integration of advanced insulating glass, acrylic, and silicone has led to remarkable improvements in building performance. For instance, the development of low-emissivity (Low-E) glass has significantly reduced heat transfer, making buildings more thermally efficient while allowing natural light to flood indoor spaces. This trend is not just about aesthetics; it’s about creating environments that are comfortable year-round while minimizing energy consumption.
Tips: When selecting insulating materials, consider their thermal performance ratings, durability, and environmental impact. Look for products with certifications such as Energy Star, which indicates superior energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the rise of smart materials that adapt to environmental conditions is transforming architectural design. Materials imbued with phase change properties can regulate temperature by absorbing or releasing heat as needed. This innovation allows architects to create dynamic spaces that promote occupant well-being. Moreover, the trend towards eco-friendly materials, such as recycled acrylic and bio-based silicone, not only meets the demands of modern architecture but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
Tips: Always evaluate the lifecycle impact of insulation materials. Opting for locally sourced materials can also reduce transportation emissions, contributing to a greener construction process.